HashMap的实现原理
HashMap是基于java.util.map接口的实现,该实现提供了所有的对Map的可选操作,同时也允许null类型的key以及value (HashTable与此大致相同,只是HashTable是同步的,不过HashTable一般被认为是已经过时的,很少有人再去用了)
HashMap不保证Map中的顺序,特别是不能保证数据在一段时间内的顺序性。
如果散列函数(Hash函数)在正确的在桶中分散元素,HashMap的实现提供了对基本的操作(put与get)时间性能为常数。
集合视图的迭代需要的时间与HashMap实例的容量capacity值(桶数)和大小(键值对个数)成正比,所以如果对迭代器的性能比较关注, 那么不要把初始化的容量capacity值设的太高或不要将装填因子load factor设的太小就非常重要。
HashMap的实例总有两个非常重要的影响性能的参数:初始容量大小(initial capacity)与装填因子(load factor)。 在HashMap中,capacity就是buckets的数量,初始容量大小就是在HashMap创建的时候指定的capacity。
装填因子指的是HashMap在多满的时候就需要提前自动扩容了(如初始化容量16,装填因子0.75,一旦元素个数 超过16*0.75=12个的时候,就需要对容量进行扩充,翻倍) 扩容需要rehash,也就是说HashMap内部结构会被重新构建。
通常来讲,默认的装填因子0.75提供了一个基于时间与空间代价比较好的平衡。桶中装的更满意味着空间开销更低, 但是查找开销变大(反映到HashMap中就是包含get与put在内各种操作开销变大,时间变长)。
当设置初始容量大小时,应该考虑HashMap中预期的数量以及装填因子,这样才能让rehash执行的次数最少, 如果初始化大小的值比实际数据的条数乘以装填因子的积还要大,那么就不会发生rehash。
如果有非常多的记录存在HashMap中,那么在初始化这个HashMap的时候将容量capacity设置的足够大,比自动rehash 扩容效率更高。
注意如果很多key有了相同的hashCode值,那么会对性能造成很大的影响(产生聚集问题,rehash次数变多,性能下降),为了改善这种情况 当key可以进行比较(继承了Comparable接口之类的),HashMap会采用对key进行比较排序。
注意:HashMap不是线程同步的。
如果多线程并发访问一个HashMap,同时至少有一个线程修改了HashMap的结构,那么该HashMap必须要在外部进行同步 (结构的改变指的是添加或删除一个映射关系-键值对,只是根据key修改了value的值不会对HashMap造成结构上的影响) 这种同步操作通常在封装有HashMap的Object中实现;如果没有这样的对象实现,那么HashMap需要采用Collections.synchronizedMap 来保证多线程并发环境下的数据同步问题,这个操作最好在创建HashMap的时候就去做。 Map m = Collections.synchronizedMap(new HashMap(…));
如果HashMap产生的迭代器创建后,HashMap数据结构又发生了变化,则除了remove方法外,迭代器iterator会抛出一个 ConcurrentModificationException异常,这就是迭代器的快速失败(fail-fast)。 因此面对并发修改,迭代器采用快速而干净的失败来取代在未来的某一个不确定的时间产生不确定的后果。
注意:迭代器的快速失败行为是无法保证的,通常来讲,在非同步并发修改的情况下这种硬性保证都没法给出,快速失败也只能尽量抛出 ConcurrentModificationException异常,所以不能写一段代码去基于该异常做出义务逻辑处理,最好快速失败进行BUG探测。
HashMap的存储结构
HashMap的存储,本质上是构造了一个table,根据计算的hashCode将对应的KV存储到该table中,一旦发生hashCode冲突,那么就会将该KV放到对应的已有元素的后面, 此时,形成了一个链表式的存储结构,即:HashMap 就是一个table数组+链表实现的存储结构(在JDK1.8之前的存储结构),如下图所示:
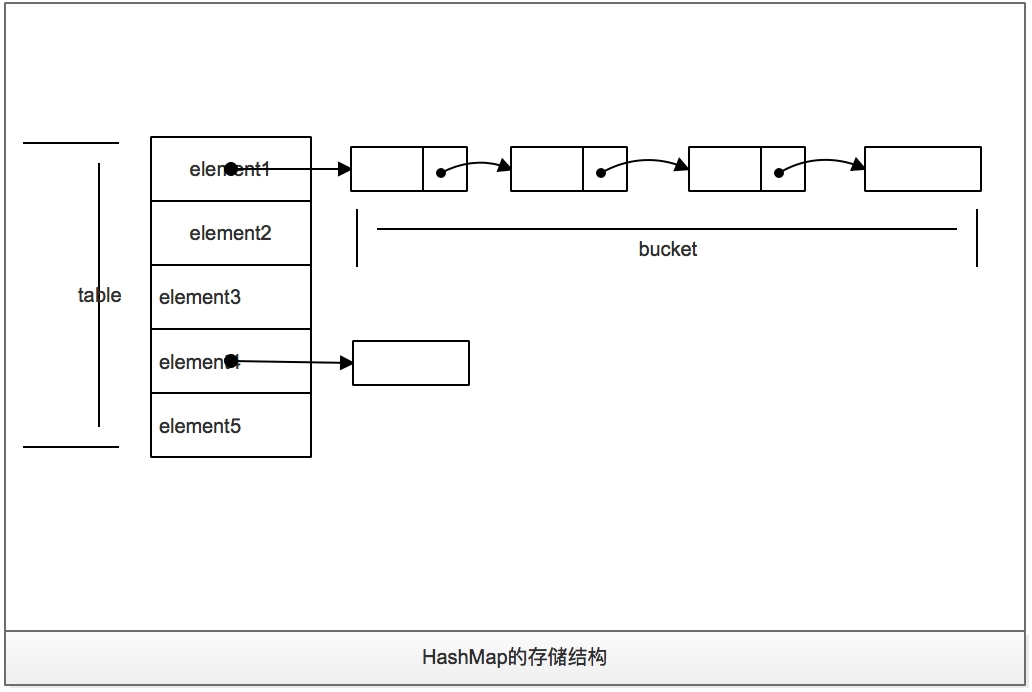
当构造出一个HashMap后,每次put一个元素时,会执行addEntry操作,addEntry中会执行创建一个Entry实体存储当前的KV,如果有Hash冲突, 那么就会将当前的entry指向最后一个冲突的entry,同时将当前的entry放到链表中,执行完当前操作后,判断是否需要resize,如果需要,则构造出一个新的entry数组(比之前大一倍), 并将原有的数组中的entry链表(或entry)拷贝到新的数组中。
在JDK1.8中有了一些变化,当链表的存储的数据个数大于等于8的时候,不再采用链表存储,而采用了红黑树存储结构。如下图所示:
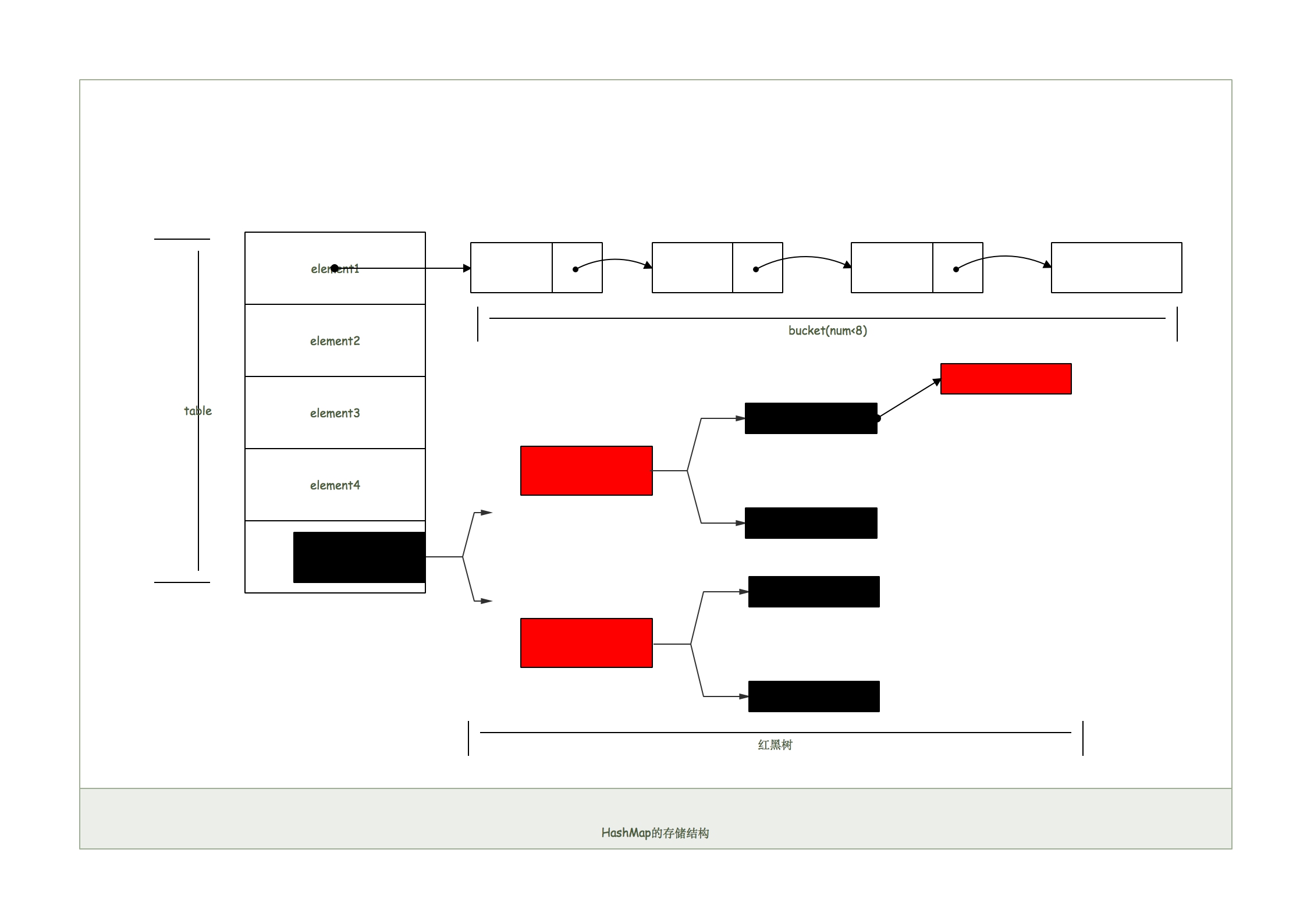 这么做主要是查询的时间复杂度上,链表为O(n),而红黑树一直是O(logn),一般来讲,冲突(即为相同的hash值存储的元素个数)
超过8个,红黑树的性能高于链表的查找性能。
这么做主要是查询的时间复杂度上,链表为O(n),而红黑树一直是O(logn),一般来讲,冲突(即为相同的hash值存储的元素个数)
超过8个,红黑树的性能高于链表的查找性能。
HashMap在JDK1.6中的实现方式
put方法:
put方法完成数据的基本写入操作,同时会验证数据的有效性,如key是否为空的处理,计算hash值,hash值 的查找,并根据hash值找出所有的数据,判断是否重复,如果重复,则替换,并返回旧值,如果不重复,则写入数据(addEntry)。
/**
* Associates the specified value with the specified key in this map.
* If the map previously contained a mapping for the key, the old
* value is replaced.
*
* @param key key with which the specified value is to be associated
* @param value value to be associated with the specified key
* @return the previous value associated with <tt>key</tt>, or
* <tt>null</tt> if there was no mapping for <tt>key</tt>.
* (A <tt>null</tt> return can also indicate that the map
* previously associated <tt>null</tt> with <tt>key</tt>.)
*/
public V put(K key, V value) {
if (key == null)
return putForNullKey(value);
int hash = hash(key.hashCode());
int i = indexFor(hash, table.length);
for (Entry<K,V> e = table[i]; e != null; e = e.next) {
Object k;
if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || key.equals(k))) {
V oldValue = e.value;
e.value = value;
e.recordAccess(this);
return oldValue;
}
}
modCount++;
addEntry(hash, key, value, i);
return null;
}
对应的addEntry方法: addEntry方法实现了数据的写入以及判断是否需要对HashMap进行扩容。
/**
* Adds a new entry with the specified key, value and hash code to
* the specified bucket. It is the responsibility of this
* method to resize the table if appropriate.
*
* Subclass overrides this to alter the behavior of put method.
*/
void addEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) {
Entry<K,V> e = table[bucketIndex];
table[bucketIndex] = new Entry<K,V>(hash, key, value, e);
if (size++ >= threshold)
resize(2 * table.length);
}
resize方法: resize方法主要是对Map进行扩容的实际操作:构造存储结构,并调用数据转移方法transfer进行数据转移
/**
* Rehashes the contents of this map into a new array with a
* larger capacity. This method is called automatically when the
* number of keys in this map reaches its threshold.
*
* If current capacity is MAXIMUM_CAPACITY, this method does not
* resize the map, but sets threshold to Integer.MAX_VALUE.
* This has the effect of preventing future calls.
*
* @param newCapacity the new capacity, MUST be a power of two;
* must be greater than current capacity unless current
* capacity is MAXIMUM_CAPACITY (in which case value
* is irrelevant).
*/
void resize(int newCapacity) {
Entry[] oldTable = table;
int oldCapacity = oldTable.length;
if (oldCapacity == MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) {
threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
return;
}
Entry[] newTable = new Entry[newCapacity];
transfer(newTable);
table = newTable;
threshold = (int)(newCapacity * loadFactor);
}
transfer 方法: 完成数据转移,注意,转移的过程就是两个数组进行数据拷贝的过程,数据产生了倒置,新元素其实是插入到了第一个位置。
/**
* Transfers all entries from current table to newTable.
*/
void transfer(Entry[] newTable) {
Entry[] src = table;
int newCapacity = newTable.length;
for (int j = 0; j < src.length; j++) {
Entry<K,V> e = src[j];
if (e != null) {
src[j] = null;
do {//每次循环都是将第一个元素指向了最新的数据,其他数据后移(链式存储,更改指向)
Entry<K,V> next = e.next;
int i = indexFor(e.hash, newCapacity);
e.next = newTable[i];
newTable[i] = e;
e = next;
} while (e != null);
}
}
}
Entry的构造: 链式存储结构。
static class Entry<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> {
final K key;
V value;
Entry<K,V> next;
final int hash;
/**
* Creates new entry.
*/
Entry(int h, K k, V v, Entry<K,V> n) {
value = v;
next = n;
key = k;
hash = h;
}
···
}
HashMap在JDK1.7中的实现
JDK1.7中的实现与JDK1.6中的实现总体来说,基本没有改进,区别不大。
put 方法:
public V put(K key, V value) {
if (table == EMPTY_TABLE) {
inflateTable(threshold);
}
if (key == null)
return putForNullKey(value);
int hash = hash(key);
int i = indexFor(hash, table.length);
for (Entry<K,V> e = table[i]; e != null; e = e.next) {
Object k;
if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || key.equals(k))) {
V oldValue = e.value;
e.value = value;
e.recordAccess(this);
return oldValue;
}
}
modCount++;
addEntry(hash, key, value, i);
return null;
}
addEntry方法:
void addEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) {
if ((size >= threshold) && (null != table[bucketIndex])) {
resize(2 * table.length);
hash = (null != key) ? hash(key) : 0;
bucketIndex = indexFor(hash, table.length);
}
createEntry(hash, key, value, bucketIndex);
}
resize方法:
void resize(int newCapacity) {
Entry[] oldTable = table;
int oldCapacity = oldTable.length;
if (oldCapacity == MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) {
threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
return;
}
Entry[] newTable = new Entry[newCapacity];
transfer(newTable, initHashSeedAsNeeded(newCapacity));
table = newTable;
threshold = (int)Math.min(newCapacity * loadFactor, MAXIMUM_CAPACITY + 1);
}
transfer方法:
void transfer(Entry[] newTable, boolean rehash) {
int newCapacity = newTable.length;
for (Entry<K,V> e : table) {
while(null != e) {
Entry<K,V> next = e.next;
if (rehash) {
e.hash = null == e.key ? 0 : hash(e.key);
}
int i = indexFor(e.hash, newCapacity);
e.next = newTable[i];
newTable[i] = e;
e = next;
}
}
createEntry方法:
/**
* Like addEntry except that this version is used when creating entries
* as part of Map construction or "pseudo-construction" (cloning,
* deserialization). This version needn't worry about resizing the table.
*
* Subclass overrides this to alter the behavior of HashMap(Map),
* clone, and readObject.
*/
void createEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) {
Entry<K,V> e = table[bucketIndex];
table[bucketIndex] = new Entry<>(hash, key, value, e);
size++;
}
HashMap在JDK1.8中的实现
put方法: put方法中与JDK1.6/1.7相比,新增了判断是否是TreeNode的逻辑,TreeNode即为红黑树, 同时添加了冲突的元素个数是否大于等于7的判断(因为第一个是-1,所以还是8个元素),如果冲突的 元素个数超过8个,则构造红黑树(treeifyBin方法),否则还是按照链表方式存储。
/**
* Implements Map.put and related methods
*
* @param hash hash for key
* @param key the key
* @param value the value to put
* @param onlyIfAbsent if true, don't change existing value
* @param evict if false, the table is in creation mode.
* @return previous value, or null if none
*/
final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent,
boolean evict) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, i;
if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
n = (tab = resize()).length;
if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null)//取模运算,寻址无冲突,写入数据
tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
else {//存在冲突
Node<K,V> e; K k;
if (p.hash == hash &&
((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
e = p;
else if (p instanceof TreeNode)//集合中已经是红黑树了
e = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value);
else {
for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) {//冲突时的数据写入逻辑,判断是否需要构造红黑树
if ((e = p.next) == null) {
p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // -1 for 1st
treeifyBin(tab, hash);
break;
}
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
break;
p = e;
}
}
if (e != null) { // existing mapping for key
V oldValue = e.value;
if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null)
e.value = value;
afterNodeAccess(e);
return oldValue;
}
}
++modCount;
if (++size > threshold)
resize();
afterNodeInsertion(evict);
return null;
}
treeifyBin方法: treeifyBin方法主要是将链式存储的冲突的数据转换成树状存储结构
/**
* Replaces all linked nodes in bin at index for given hash unless
* table is too small, in which case resizes instead.
*/
final void treeifyBin(Node<K,V>[] tab, int hash) {
int n, index; Node<K,V> e;
if (tab == null || (n = tab.length) < MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY)
resize();
else if ((e = tab[index = (n - 1) & hash]) != null) {
TreeNode<K,V> hd = null, tl = null;
do {
TreeNode<K,V> p = replacementTreeNode(e, null);
if (tl == null)
hd = p;
else {
p.prev = tl;
tl.next = p;
}
tl = p;
} while ((e = e.next) != null);
if ((tab[index] = hd) != null)
hd.treeify(tab);
}
}
resize方法: 注意:JDK1.8中resize方法扩容时对链表保持了原有的顺序。
/**
* Initializes or doubles table size. If null, allocates in
* accord with initial capacity target held in field threshold.
* Otherwise, because we are using power-of-two expansion, the
* elements from each bin must either stay at same index, or move
* with a power of two offset in the new table.
*
* @return the table
*/
final Node<K,V>[] resize() {
Node<K,V>[] oldTab = table;
int oldCap = (oldTab == null) ? 0 : oldTab.length;
int oldThr = threshold;
int newCap, newThr = 0;
if (oldCap > 0) {
if (oldCap >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) {
threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
return oldTab;
}
else if ((newCap = oldCap << 1) < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY &&
oldCap >= DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY)
newThr = oldThr << 1; // double threshold
}
else if (oldThr > 0) // initial capacity was placed in threshold
newCap = oldThr;
else { // zero initial threshold signifies using defaults
newCap = DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY;
newThr = (int)(DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR * DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY);
}
if (newThr == 0) {
float ft = (float)newCap * loadFactor;
newThr = (newCap < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY && ft < (float)MAXIMUM_CAPACITY ?
(int)ft : Integer.MAX_VALUE);
}
threshold = newThr;
@SuppressWarnings({"rawtypes","unchecked"})
Node<K,V>[] newTab = (Node<K,V>[])new Node[newCap];
table = newTab;
if (oldTab != null) {
for (int j = 0; j < oldCap; ++j) {
Node<K,V> e;
if ((e = oldTab[j]) != null) {
oldTab[j] = null;
if (e.next == null)
newTab[e.hash & (newCap - 1)] = e;
else if (e instanceof TreeNode)
((TreeNode<K,V>)e).split(this, newTab, j, oldCap);
else { // preserve order
Node<K,V> loHead = null, loTail = null;
Node<K,V> hiHead = null, hiTail = null;
Node<K,V> next;
do {
next = e.next;
if ((e.hash & oldCap) == 0) {
if (loTail == null)
loHead = e;
else
loTail.next = e;
loTail = e;
}
else {
if (hiTail == null)
hiHead = e;
else
hiTail.next = e;
hiTail = e;
}
} while ((e = next) != null);
if (loTail != null) {
loTail.next = null;
newTab[j] = loHead;
}
if (hiTail != null) {
hiTail.next = null;
newTab[j + oldCap] = hiHead;
}
}
}
}
}
return newTab;
}
HashMap的不足以及产生原因
多线程并发问题
在多线程并发环境下会有如下一种情况:
两个线程同时操作时同时遇到HashMap需要扩容,且映射到相同的地址(key计算得到的HashCode相同),此时在扩容时可能发生一种情况, 两个线程同时对HashMap进行扩容,扩容时做第一次循环时一个线程阻塞,另一个完成扩容,前一个继续,那么就可能发生链表数据的相互指向问题, 造成get数据时遍历的死循环
测试代码如下:
final Map<Integer, String> map = new HashMap<>(2);
map.put(3, "3");
Thread t = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
map.put(5, "5");
}
}, "thread");
Thread t2 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
map.put(7, "7");
}
}, "thread2");
t.start();
t2.start();
t.join();
t2.join();
注意:我参考了大量的网上的一些博客,他们基本都是基于JDK1.6进行的分析,即:先写入数据,再扩容:
void addEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) {
Entry<K,V> e = table[bucketIndex];
table[bucketIndex] = new Entry<K,V>(hash, key, value, e);//先写数据
if (size++ >= threshold)
resize(2 * table.length);//再扩容
}
由此,很容易产生上述问题,而在JDK1.7中发生了变化,先扩容,再进行数据写入:
void addEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) {
if ((size >= threshold) && (null != table[bucketIndex])) {
resize(2 * table.length);//先扩容
hash = (null != key) ? hash(key) : 0;
bucketIndex = indexFor(hash, table.length);
}
createEntry(hash, key, value, bucketIndex);//再写入数据
}
此时,先扩容,再写入数据,就不会产生这种问题,但是会产生另一中问题,即: HashMap中有A元素,thread1 写入B元素(碰撞),thread2写入C元素(碰撞) 线程thread1先扩容,在写入数据,同时线程thread2也进行该操作那么,最终互不影响, thread1得到:B->A链表,thread2得到:C->A链表,那么,在thread1中取数据,能否取到C元素? 多线程并发问题依旧存在
在JDK1.8中,HashMap的这块儿做了大量改进,死循环问题已经解决了:
final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent,
boolean evict) {
//......
for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) {
if ((e = p.next) == null) {
p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null);//直接追加到最后节点中
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // -1 for 1st
treeifyBin(tab, hash);//构造红黑树
break;
}
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
break;
p = e;
}
//......
}
但是JDK1.8 中通过测试发现依然存在JDK1.7中的数据丢失情况.
同时在并发情况下会出现如下新的问题: Hash碰撞情况下:前一个线程判断是链表存储,准备写入数据,但是写入时阻塞,其他线程也准备写入,发现数据链表为8,此时构造红黑树,然后完成数据转移 前一个线程此后写入数据时,就会出现类型错误:
Exception in thread "24590 _subThread" java.lang.ClassCastException: java.util.HashMap$Node cannot be cast to java.util.HashMap$TreeNode
at java.util.HashMap$TreeNode.moveRootToFront(HashMap.java:1827)
at java.util.HashMap$TreeNode.treeify(HashMap.java:1944)
at java.util.HashMap$TreeNode.split(HashMap.java:2170)
at java.util.HashMap.resize(HashMap.java:713)
at java.util.HashMap.putVal(HashMap.java:662)
at java.util.HashMap.put(HashMap.java:611)
at com.lin.map.HashMapDeadLoopTest$1$1.run(HashMapDeadLoopTest.java:37)
at java.lang.Thread.run(Thread.java:745)
另一个问题,如果在写入时发生阻塞(可能的原因如数据构造红黑树的过程中,或其他过程),然后立即取数据,可能就取不到数据
相关测试代码(可能需要多执行几次):
public class HashMapDeadLoopTest {
@Test
public void test() throws InterruptedException {
// final Map<String, String> map = Collections.synchronizedMap(new HashMap<>(2048));
final Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<>(2048);
Thread t = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++) {
final int x = i;
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
put(map, x);
}
},i+" _subThread").start();
if(i!=0 && i%10000==0){
System.out.println("1:"+map.size());
}
}
}
},"thread");
Thread t2 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++) {
final int x = i;
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
put(map, x);
}
},i+" _subThread2").start();
if(i!=0 && i%10000==0){
System.out.println("2:"+map.size());
}
}
}
},"thread2");
Thread t3 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++) {
final int x = i;
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
put(map, x);
}
},i+" _subThread3").start();
if(i!=0 && i%10000==0){
System.out.println("3:"+map.size());
}
}
}
},"thread3");
t.start();
t2.start();
t3.start();
t.join();
t2.join();
t3.join();
}
String getKey(){
return RandomStringUtils.randomAlphanumeric(32);
}
void put(Map<String,String> map,int index){
String key = getKey();
map.put(key, key);
if(map.get(key)==null){
System.out.println(key+",元素缺失,index:"+index);
}
}
}
总结
- HashMap的JDK1.6、JDK1.7、JDK1.8中的实现各不相同,尤其以JDK1.8变化最大,注意区分
- 学习研究虽然不拒绝参考前人的研究成果,但也要注意区分验证